You are about to leave OurWayForward.com.
You are about to leave a GSK website. By clicking this link, you will be taken to a website that is independent from GSK. The site you are linking to is not controlled or endorsed by GSK and GSK is not responsible for its content.
Endometrial Cancer Diagnosis
Endometrial cancer is most often diagnosed after a person visits their healthcare professional because they are experiencing symptoms.
There is currently no standard or routine screening test for endometrial cancer for early diagnosis in patients who are at average risk and have no symptoms. Because of this, it’s important to pay attention to any changes in your body that do not feel normal and talk to your healthcare professional if you notice anything unusual. You should also talk to your healthcare professional about when to get pelvic exams and pap smears. These tests are not specifically used to screen for endometrial cancer, but may be helpful in discovering some cases of endometrial cancer.
Examples of Endometrial Cancer Tests:
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS)
- Endometrial biopsy and tissue sampling
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
- Hysteroscopy
- Molecular profile tests (i.e., biomarker tests)
- Additional scans or blood tests as recommended by your healthcare professional
Endometrial Cancer Grading
Following a biopsy, if cancer cells are identified, they will be graded. Grading helps doctors understand how fast the cancer may grow and spread. The grading scale looks at the cancer cells to see how much they look like normal cells, on a scale from 1 to 3. Grading helps doctors determine the best treatment approach for you.
Grade I (1) and Grade II (2)
| Likely referred to as “lower grade” |
| Cancer cells look more like normal cells |
| Cells grow and spread to other parts of the body more slowly (less aggressive) |
| Less likely to return (recur) |
Grade III (3)
| Likely referred to as “high grade” |
| Cancer cells look very abnormal |
| Cells grow and spread to other parts of the body more quickly (more aggressive) |
| More likely to return (recur) |
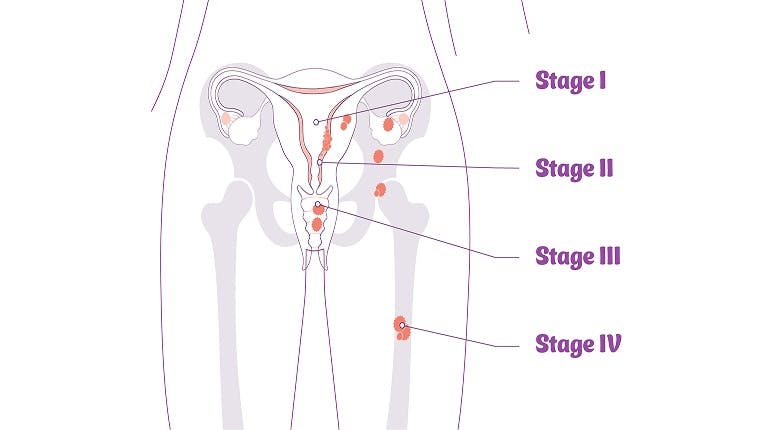
Endometrial Cancer Stages
After receiving a diagnosis of endometrial cancer, your healthcare professional will assign a stage to your cancer. The stage describes the amount of cancer in the body, how far it has spread, and how best to treat it. Staging is typically determined by imaging tests and blood tests. Lower numbers mean the cancer has spread less and higher numbers mean the cancer has spread more.
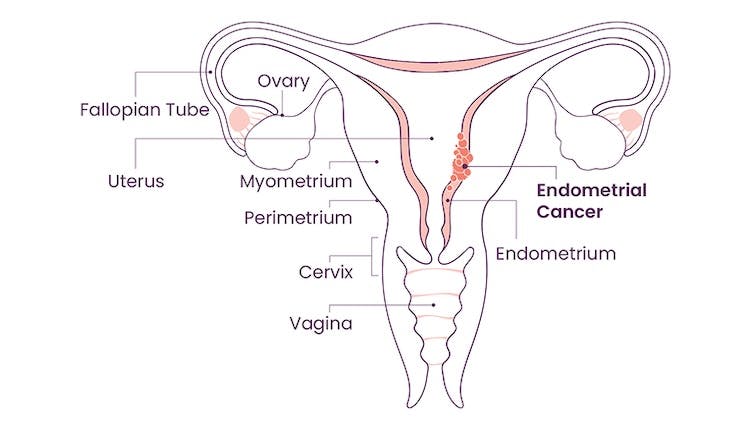
FIGO Staging
The following staging is called the FIGO system since it was developed by the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics. Refer to the diagrams on this page to identify the locations of the body impacted by the staging.

Stage I
Cancer is found in the body (also called the corpus) of the uterus only
- Stage IA – cancer is in the endometrium (inner lining of the uterus), either less than or up to halfway through the muscle layer of the uterus (called the myometrium)
- Stage IB – cancer has spread more than halfway through the myometrium

Stage II
Cancer has spread into the connective tissues of the cervix but not outside the uterus

Stage III
Cancer has spread beyond the uterus body and cervix but not beyond the pelvis
- Stage IIIA – cancer has spread to the outer layer of the uterus and/or to the fallopian tubes and ovaries
- Stage IIIB – cancer has spread to the vagina and/or the tissues around the uterus (called the parametrium)
- Stage IIIC1 – cancer has spread to lymph nodes in the pelvis but not the bladder or rectum
- Stage IIIC2 – cancer has spread to the lymph nodes around the aorta (the largest artery of the body, which carries blood away from the heart) but not to distant sites

Stage IV
Cancer has spread beyond the pelvis
- Stage IVA – cancer has spread to the bladder and/or inner lining of the rectum
- Stage IVB – cancer has spread to other parts of the body beyond the pelvis, including the upper abdomen (belly), lymph nodes in the groin, or to more distant areas, such as the lungs, liver, or bones