You are about to leave OurWayForward.com.
You are about to leave a GSK website. By clicking this link, you will be taken to a website that is independent from GSK. The site you are linking to is not controlled or endorsed by GSK and GSK is not responsible for its content.
Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
Ovarian cancer is most often diagnosed after a person visits their healthcare provider because they are experiencing symptoms. However, the symptoms of ovarian cancer may be subtle.
There is currently no standard or routine screening test for diagnosing ovarian cancer early in patients who are at average risk and have no symptoms. Because of this, it’s important to pay attention to any changes in your body that do not feel normal and talk to a healthcare professional if you notice anything unusual.
Being persistent and proactive in keeping your doctor informed of your symptoms can help foster earlier diagnosis.
Your healthcare professional can perform a variety of tests to diagnose ovarian cancer, including imaging biopsy and blood tests.
Examples of Tests:
- Pelvic/abdominal ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- PET-CT scan
- Chest X-ray
- Laparoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Pelvic/abdominal ultrasound
- CA-125 blood test
- Note: CA-125 is not an indicator of all cancers.
PAP smears do not identify ovarian cancer.
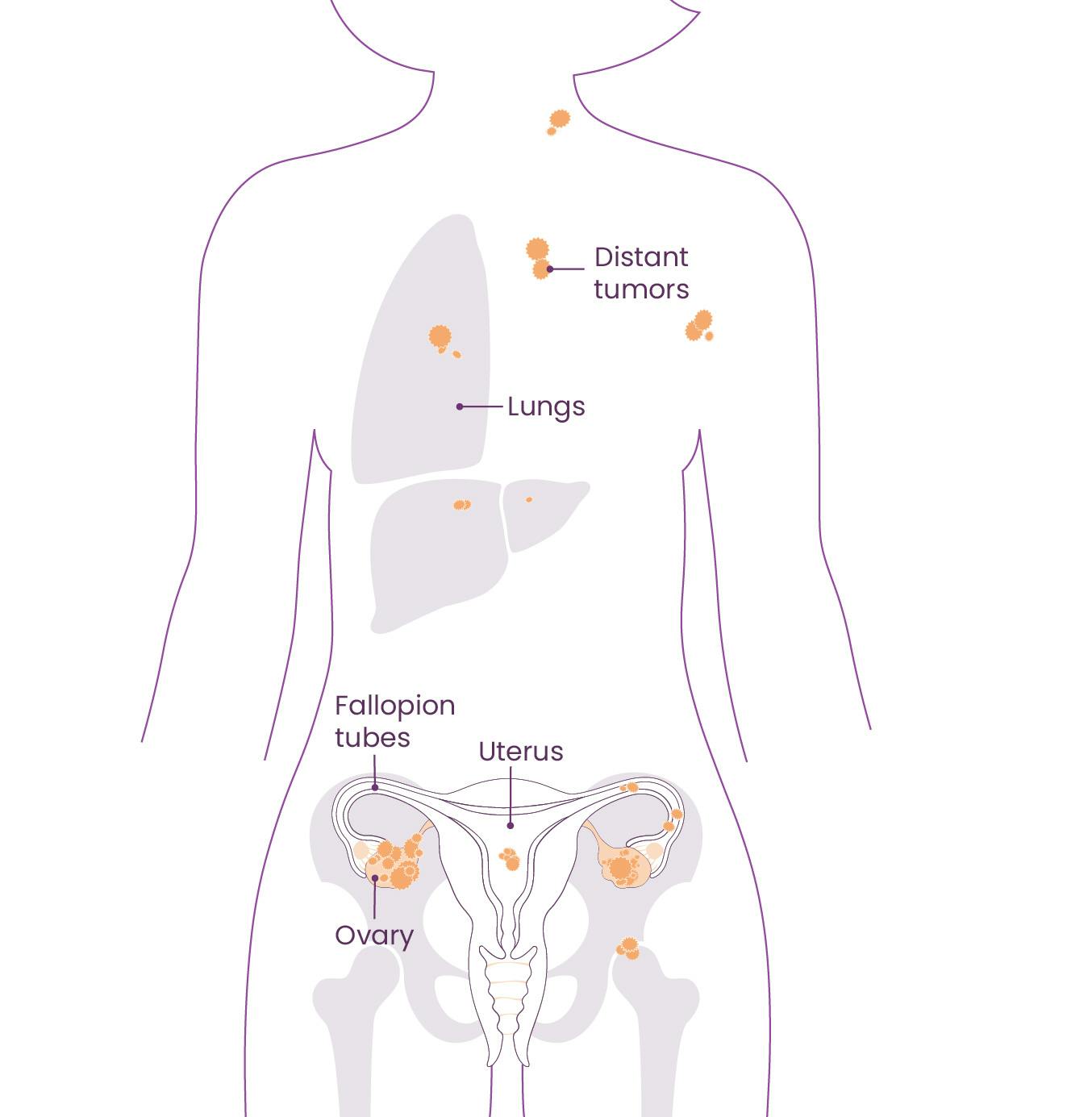
Ovarian Cancer Stages at Diagnosis
To stage ovarian cancer, tissue samples are taken during surgery. Ovarian cancer is typically given one of four stages at diagnosis.
FIGO Staging
The following staging is called the FIGO system since it was developed by the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics. Refer to the diagram on this page to identify the locations of the body impacted by the staging.
Stage I
The cancer is in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes
- Stage IA: The cancer is inside one ovary or one fallopian tube. There is no cancer on the outside of the ovary or fallopian tube
- Stage IB: The cancer is inside both ovaries or fallopian tubes but not on the outside
- Stage IC: The cancer is inside or outside one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread to the outer layer; has been found in the fluid from the abdomen and pelvis; the tissue surrounding the tumor broke
Stage II
The cancer is in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread to other organs within the pelvis (such as the uterus or bladder)
- Stage IIA: The cancer has spread to the uterus
- Stage IIB: The cancer is on the outer surface or has grown into other organs, such as the bladder
Stage III
The cancer is in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread to retroperitoneal (pelvic) lymph nodes
- Stage IIIA1: The cancer may have spread or grown into nearby organs in the pelvis
- Stage IIIA2: The cancer has spread or grown into organs outside the pelvis and tiny traces of cancer are found in the lining of the abdomen
- Stage IIIB: The cancer has spread or grown into organs outside the pelvis
- Stage IIIC: The cancer has spread to the outside of the liver or spleen
Stage IV
The cancer has spread to organs beyond the peritoneal (inner abdominal) area
- Stage IVA: Cancer cells have been found in the fluid around the lungs
- Stage IVB: The cancer has spread to the inside of the spleen or liver and to other organs outside the peritoneal cavity, such as the lungs and bones